API
- 1. Introduce
- 2. Initialization Functions and Main Functions
- 3. Global variables
- 4. Timer
- 5. System Variables
- 6. Send messages defined in DBC or LDF files via the interface
- 7. CAN
- 8. CANFD
- 9. LIN
- 10. Digital
- 11. Analog
- 12. Other
1. Introduce
1.1 What is a C Mini Program
C Mini Program is a mini program written in C/C++ language. It is a small program that can be run in the ETStudio. Through the APIs provided by ETStudio, it conveniently implements various functions, such as timers, sending and receiving of CAN and LIN messages, reading and writing of digital signals, analog signals, power control, and system variables.
1.2 Document Introduction
This document describes the APIs provided by the C Mini Program.
1.3 Running the Mini Program
- Running during the development and testing phase: Refer to Code Editor
- Running during the release phase: Refer to Simulation Node
2. Initialization Functions and Main Functions
2.1 A simple example
#include "BaseMiniProgram.h"
void PreviewApplicationInitialize()
{
}
void MainTest()
{
uint8_t data[8] = {0};
CAN_Tx(1, 1, 8, data);
}
void MainTestFinalized()
{
}
2.2 Return Code Definitions
typedef enum
{
ErrCode_Success = 0,
ErrCode_NullArgument,
ErrCode_NotImplemented,
ErrCode_ChannelDisabled,
ErrCode_DriverNotSupport = 254,
ErrCode_DriverError = 255,
} KAPI_ErrCode;
2.3 C Mini Program Initialization Functions
PreviewApplicationInitializeThis function is called when the C Mini Program starts, used to initialize the C Mini Program
void PreviewApplicationInitialize()
{
}
MainTestThis function is called once after the C Mini Program starts. You can register periodic functions or timers here.
void MainTest()
{
}
MainTestFinalizedThis function is called when the C Mini Program ends.
void MainTestFinalized()
{
}
2.4 Register Periodic Main Function
void register_MainFunction(uint32 period , void (*pMainFunction)(void));
Description
- Register a periodic function to be called every period milliseconds. The function is called by the system timer. If the function is not called in time, it will be called as soon as possible.
parameters
- period Call period in milliseconds
- pMainFunction Pointer to the periodic function to register
Return
- void
usage
void periodMainCallbackFunc()
{
// Do something
}
void MainTest()
{
register_MainFunction(1000, periodMainCallbackFunc);
}
3. Global variables
3.1 GetCurrentChannelMappingID
int GetCurrentChannelMappingID();- Description
- The channel mapping ID is used to identify the channel of the current node. The channel mapping ID is set in the ETStudio.
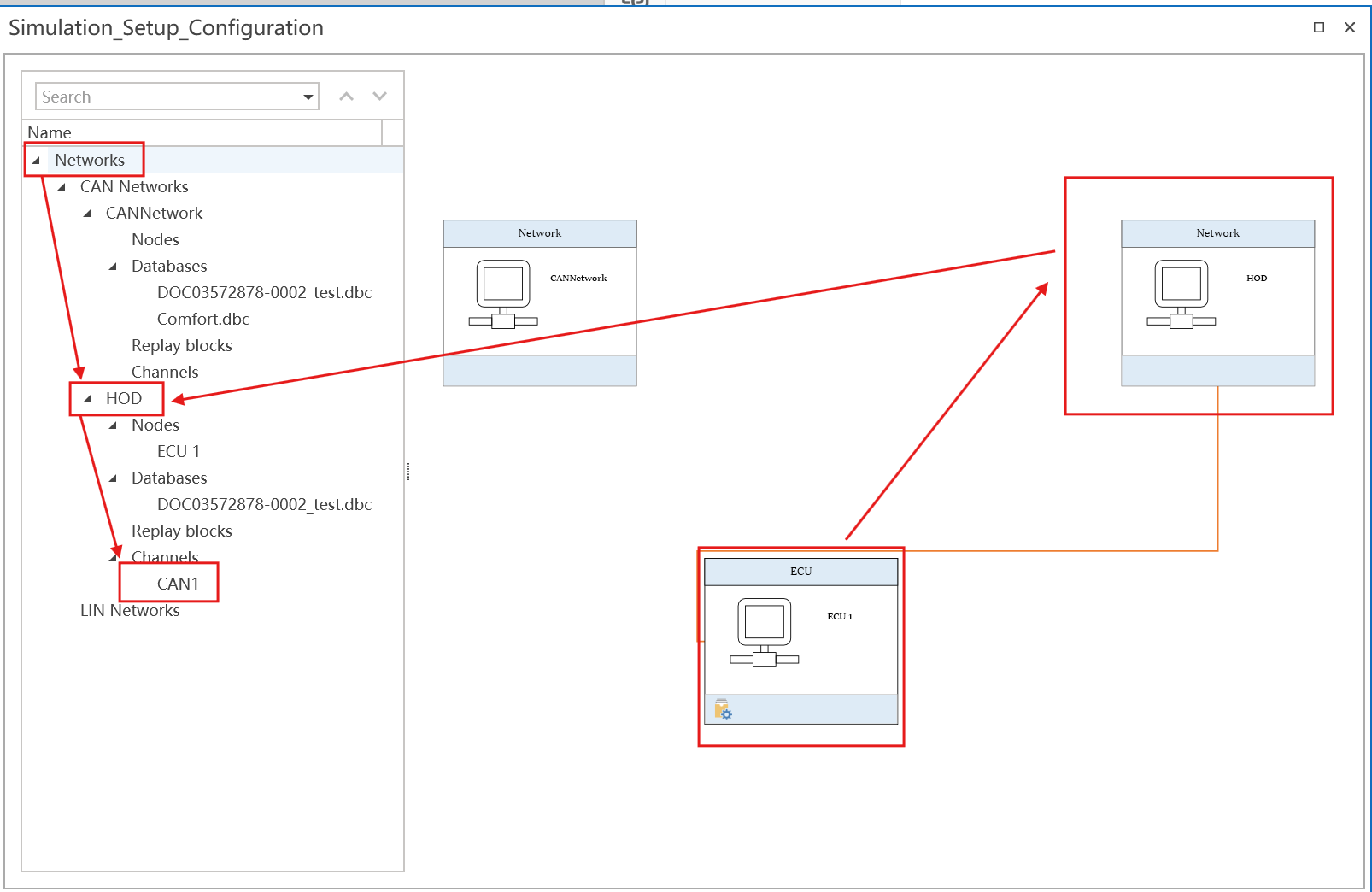
- The channel mapping ID is used to identify the channel of the current node. The channel mapping ID is set in the ETStudio.
4. Timer
4.1 start_timer
void* start_timer(uint64_t interval, boolean onceTimer, void (*onTimer)(void* pTimer));
Description
- start a timer
parameters
- interval Timer interval in milliseconds
- onceTimer
- TRUE Single-shot timer (auto-stops after timeout)
- FALSE Continuous timer (auto-restarts after timeout)
- onTimer Callback function when timer expires
Return
- void* Timer handle
usage
// create a 1 second timer
void onTimer(void* pTimer)
{
// Do something
}
start_timer(1000, FALSE, onTimer);
Reference
4.2 stop_timer
void stop_timer(void* pTimer);
Description
- stop a timer
parameters
- pTimer Timer handle returned by start_timer
usage
void onTimer(void* pTimer)
{
// Do something
}
void* timer = start_timer(1000, FALSE, onTimer);
...
stop_timer(timer);
Reference
5. System Variables
5.1 Access System Variables
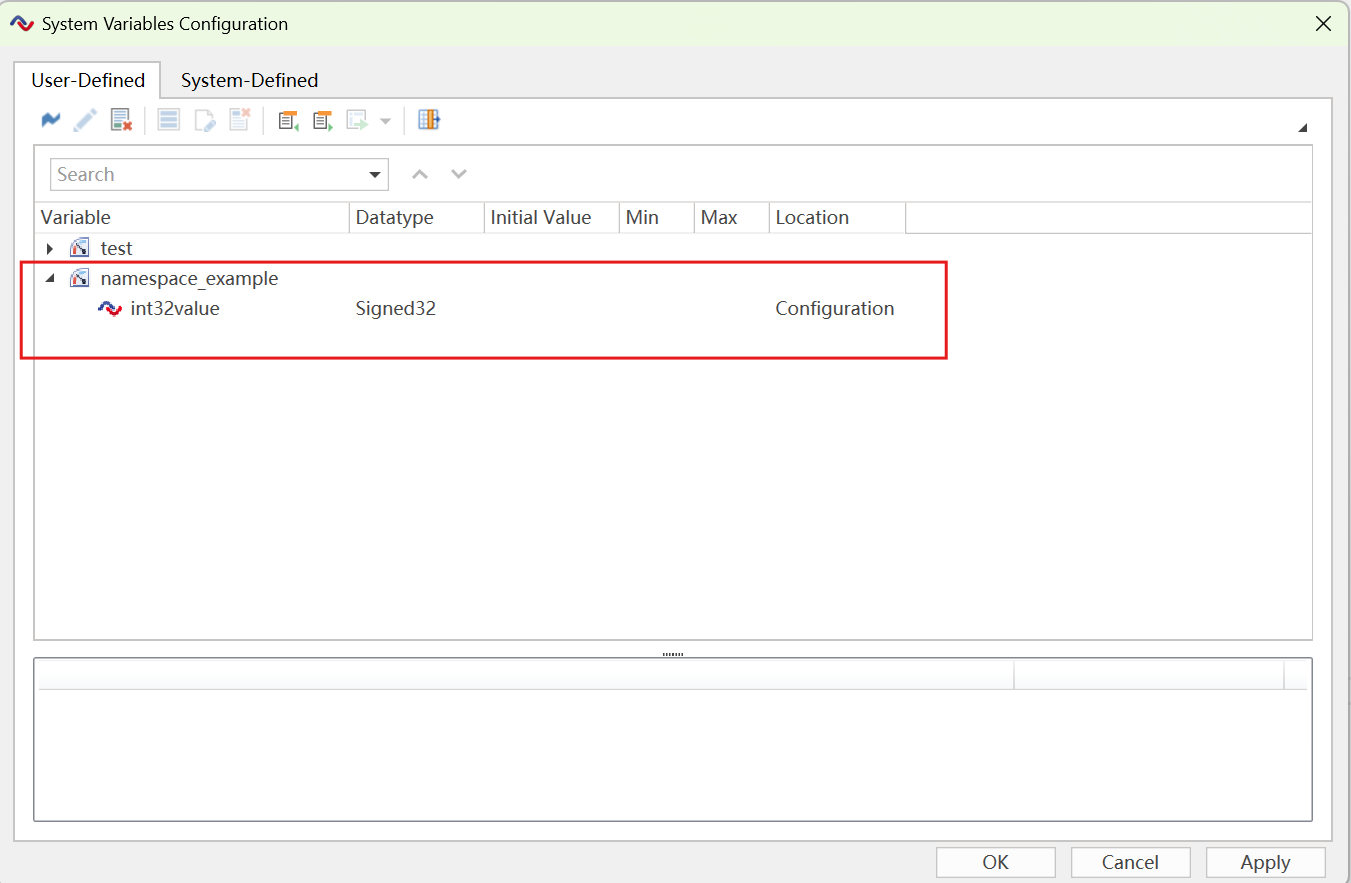
- Create System Variables in the ETStudio System Variables Interface
- Read System variable value
int32_t varValue = namespace_example::int32value; - Set the System variable value
namespace_example::int32value = 30;
5.2 SetOnChange
void SetOnChange(void (*onChange)())
Description
- Register a callback function when the system variable changes
parameters
- onChange Callback function when system variable changes
Usage
void on_namespace_example_int32valueChange()
{
int32_t varValue = namespace_example::int32value;
}
void MainTest()
{
namespace_example::int32value.SetOnChange(on_namespace_example_int32valueChange);
}
Note: In the current version, newly created or modified system variables may not be recognized by Code Editor. If new system variables are not detected in Code Editor, please restart ETStudio.
6. Send messages defined in DBC or LDF files via the interface
6.1 Send Frame
void Transmit();
Description
- Send a CAN, CAN FD, or LIN frame based on the Simulation Node configuration.
Usage - Assume we have imported a dbc/ldf file into the Simulation Network CANNetwork, which contains a message named Gateway_1. The following code can be used to send this CAN, CAN FD, or LIN message.
CANNetwork::Gateway_1 msg;
msg.Gear = 1;
msg.EngineRunning = 2;
msg.Ig_15 = 3;
msg.Ig_15R = 4;
msg.StarterKey = 5;
msg.Transmit();
- Send a message to the specified Channel Mapping ID
CANNetwork::Gateway_1 msg(2);
msg.Gear = 1;
msg.EngineRunning = 2;
msg.Ig_15 = 3;
msg.Ig_15R = 4;
msg.StarterKey = 5;
msg.Transmit();
- Send a message to the specified BusType (
BUS_TYPE_CAN)
CANNetwork::Gateway_1 msg;
msg.Gear = 1;
msg.EngineRunning = 2;
msg.Ig_15 = 3;
msg.Ig_15R = 4;
msg.StarterKey = 5;
msg.BusType = BUS_TYPE_CAN;
msg.Transmit();
- CANNetwork is the name of the Simulation Network
- Gateway_1 is the name of the frame.
- BusType
BUS_TYPE_CAN,BUS_TYPE_CANFD,BUS_TYPE_LIN
6.2 Send Frame with Signal Value Set by Panel
static int StaticTransmit(int channelMappingID = 0);
Description
- Send a CAN, CAN FD, or LIN frame based on the Simulation Node configuration.
- The difference from Send Frame is that the signals in the message are configured via Panel.
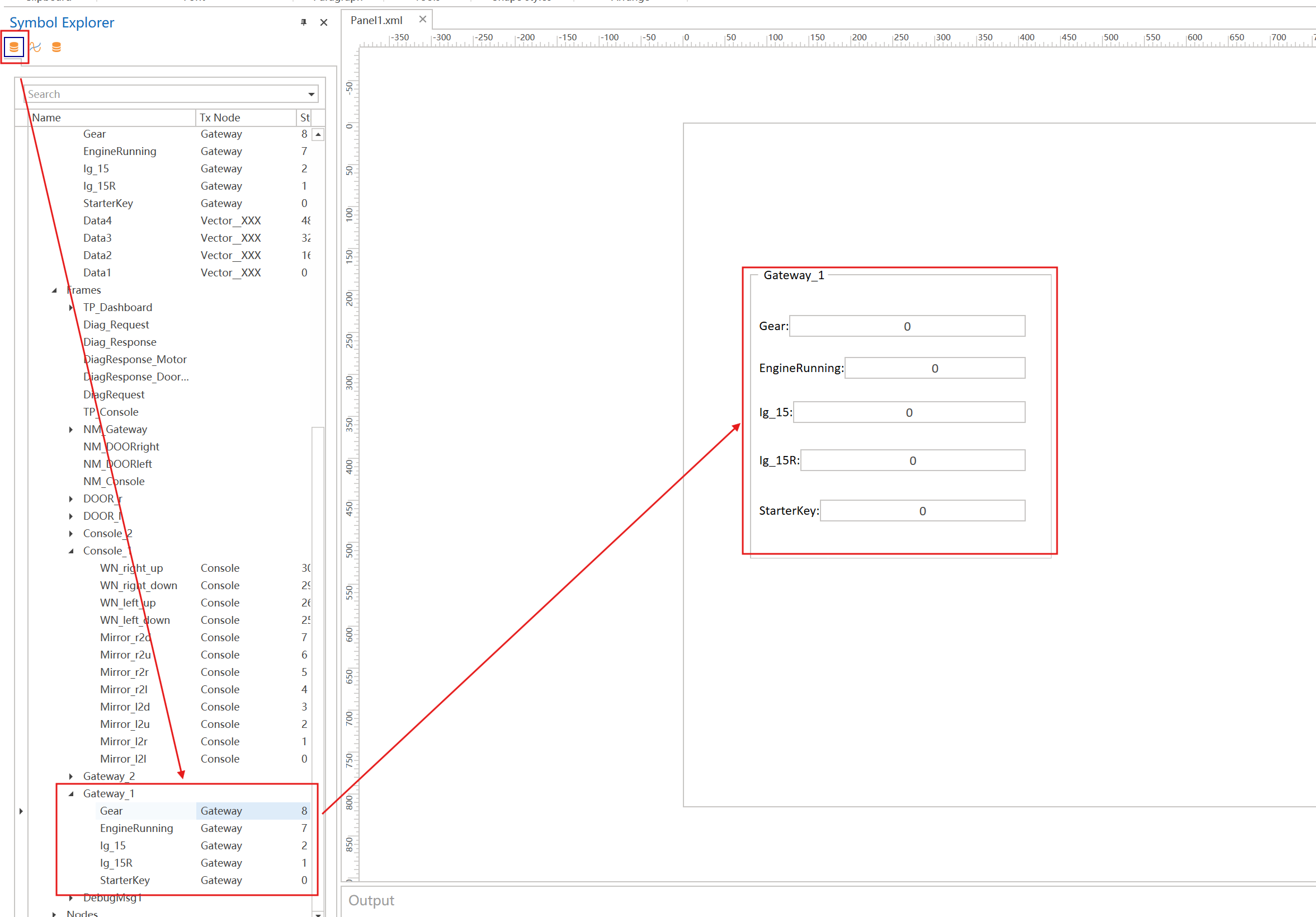
parameters
- channelMappingID CAN channel ID, 0 means the default channel ID of the current node
- busType
BUS_TYPE_CAN,BUS_TYPE_CANFDorBUS_TYPE_LINUsage
CANNetwork::Gateway_1::StaticTransmit();
- CANNetwork is the name of the Simulation Network
- Gateway_1 is the name of the frame.
6.3 receive frame
void on_recv_message(<NetworkName>::<FrameName> *msg)
Description
- Register a callback function when the CAN, CANFD or LIN frame is received.
parameters
- msg Pointer to the received frame, the type of the pointer is determined by the dbc/ldf file imported into the Simulation Network.
Usage
void on_recv_message(CANNetwork::Gateway_1 *msg)
{
// Do something
}
void MainTest()
{
CANNetwork::Gateway_1::OnMessage = on_recv_message;
}
- CANNetwork is the name of the Simulation Network
- Gateway_1 is the name of the frame.
7. CAN
Type definitions
typedef struct
{
uint32_t timestamp_us;
uint8_t bus_type;
uint8_t event_type;
uint8_t channel;
uint8_t dir;
uint8_t dlc;
uint8_t extended_frame;
uint8_t subDeviceNumber;
uint8_t reserved;
uint32_t id;
uint8_t data[64];
} EM_ReceiveFrame_t;
typedef struct
{
uint32_t can_id;
bool rtr_frame;
bool extended_frame;
uint8_t can_dlc;
uint8_t channel;
uint8_t data[64];
uint32_t timestamp_us;
} EM_CANSendFrame_t;
7.1 Send CAN Frame
KAPI_ErrCode CAN_Tx(uint32_t channelMappingID, uint32_t id, uint8_t dlc, uint8_t* data);
Description
- Send a CAN frame
parameters
- channelMappingID CAN channel ID, 0 means the default channel ID of the current node
- id CAN ID
- dlc Data Length Code
- data Pointer to data buffer
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
uint8_t data[8] = {0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08};
CAN_Tx(0, 0x123, 8, data);
7.2 Register CAN Receive Callback
KAPI_ErrCode register_CANRxEvent(uint32_t channelMappingID, uint32_t id, ReceiveFrameHandler callback);
Description
- Register a callback function when a CAN frame is received
parameters
- channelMappingID CAN channel ID, 0 means the default channel ID of the current node
- id CAN ID to filter
- callback Receive frame handler (typedef void (ReceiveFrameHandler)(EM_ReceiveFrame_t const))
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
void onCANRx(EM_ReceiveFrame_t const* frame)
{
// Do something
}
uint32_t channelMappingID = 0;
uint32_t id = 0x123;
register_CANRxEvent(channelMappingID, id, onCANRx);
7.3 Register CAN Transmission Complete Callback
KAPI_ErrCode register_CANTxEvent(uint32_t channelMappingID, uint32_t id, CANSendFrameHandler callback);
Description
- Register a callback function when a CAN frame is transmitted
parameters
- channelMappingID CAN channel ID, 0 means the default channel ID of the current node
- id CAN ID to filter
- callback Transmission complete handler (typedef void (CANSendFrameHandler)(EM_CANSendFrame_t))
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
void onCANTx(EM_CANSendFrame_t* frame)
{
// Do something
}
uint32_t channelMappingID = 0;
uint32_t id = 0x123;
register_CANTxEvent(channelMappingID, id, onCANTx);
7.4 Register CAN Pre-Transmission Callback
KAPI_ErrCode register_CANPreTxEvent(uint32_t channelMappingID, uint32_t id, CANSendFrameHandler callback);
Description
- Register a callback function when a CAN frame is about to be transmitted
parameters
- channelMappingID CAN channel ID, 0 means the default channel ID of the current node
- id CAN ID to filter
- callback Pre-transmission handler (typedef void (CANSendFrameHandler)(EM_CANSendFrame_t))
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
void onCANPreTx(EM_CANSendFrame_t* frame)
{
// Do something
}
uint32_t channelMappingID = 0;
uint32_t id = 0x123;
register_CANPreTxEvent(channelMappingID, id, onCANPreTx);
8. CANFD
8.1 Send CANFD Frame
KAPI_ErrCode CANFD_Tx(uint32_t channelMappingID, uint32_t id, uint8_t dlc, uint8_t* data);
Description
- Send a CANFD frame
parameters
- channelMappingID CANFD channel ID, 0 means the default channel ID of the current node
- id CANFD ID
- dlc Data Length Code
- data Pointer to data buffer
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
uint8_t data[8] = {0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08};
CANFD_Tx(0, 0x123, 8, data);
8.2 Register CANFD Receive Callback
KAPI_ErrCode register_CANFDRxEvent(uint32_t channelMappingID, uint32_t id, ReceiveFrameHandler callback);
Description
- Register a callback function when a CANFD frame is received
parameters
- channelMappingID CANFD channel ID, 0 means the default channel ID of the current node
- id CANFD ID to filter
- callback Receive frame handler (typedef void (ReceiveFrameHandler)(EM_ReceiveFrame_t const))
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
void onCANFDRx(EM_ReceiveFrame_t const* frame)
{
// Do something
}
uint32_t channelMappingID = 0;
uint32_t id = 0x123;
register_CANFDRxEvent(channelMappingID, id, onCANFDRx);
8.3 Register CANFD Transmission Callback
KAPI_ErrCode register_CANFDTxEvent(uint32_t channelMappingID, uint32_t id, CANSendFrameHandler callback);
Description
- Register a callback function when a CANFD frame is transmitted
parameters
- channelMappingID CANFD channel ID, 0 means the default channel ID of the current node
- id CANFD ID to filter
- callback Transmission complete handler (typedef void (CANSendFrameHandler)(EM_CANSendFrame_t))
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
void onCANFDTx(EM_CANSendFrame_t* frame)
{
// Do something
}
uint32_t channelMappingID = 0;
uint32_t id = 0x123;
register_CANFDTxEvent(channelMappingID, id, onCANFDTx);
8.4 Register CANFD Pre-Transmission Callback
KAPI_ErrCode register_CANFDPreTxEvent(uint32_t channelMappingID, uint32_t id, CANSendFrameHandler callback);
Description
- Register a callback function when a CANFD frame is about to be transmitted
parameters
- channelMappingID CANFD channel ID, 0 means the default channel ID of the current node
- id CANFD ID to filter
- callback Pre-transmission handler (typedef void (CANSendFrameHandler)(EM_CANSendFrame_t))
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
void onCANFDPreTx(EM_CANSendFrame_t* frame)
{
// Do something
}
uint32_t channelMappingID = 0;
uint32_t id = 0x123;
register_CANFDPreTxEvent(channelMappingID, id, onCANFDPreTx);
9. LIN
Type definition
typedef struct
{
uint8_t lin_head;
uint8_t lin_dlc;
uint8_t channel;
uint8_t data[8];
uint32_t timestamp_us;
} EM_LINSendFrame_t;
9.1 LIN Master Send Header
KAPI_ErrCode LinMaster_TxHeader(uint32_t channelMappingID, uint8_t header);
Description
- Send a LIN header
parameters
- channelMappingID LIN channel ID, 0 means the default channel ID of the current node
- header LIN header
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
LinMaster_TxHeader(0, 0x3C);
9.2 LIN Master Send Header and Data
KAPI_ErrCode LinMaster_Tx(uint32_t channelMappingID, uint8_t header, uint8_t dlc, uint8_t* data);
Description
- Send a LIN frame
parameters
- channelMappingID LIN channel ID, 0 means the default channel ID of the current node
- header LIN header
- dlc Data Length Code
- data Pointer to data buffer
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
uint8_t data[8] = {0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08};
LinMaster_Tx(0, 0x3C, 8, data);
9.3 Register LIN Master Receive Callback
KAPI_ErrCode register_LinMasterRxEvent(uint32_t channelMappingID, uint8_t header, ReceiveFrameHandler callback);
Description
- Register a callback function when a LIN frame is received
parameters
- channelMappingID LIN channel ID, 0 means the default channel ID of the current node
- header LIN header to filter
- callback Receive frame handler (typedef void (ReceiveFrameHandler)(EM_ReceiveFrame_t const))
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
void onLinMasterRx(EM_ReceiveFrame_t const* frame)
{
// Do something
}
uint32_t channelMappingID = 0;
uint8_t header = 0x3C;
register_LinMasterRxEvent(channelMappingID, header, onLinMasterRx);
9.4 Register LIN Master Transmission Callback
KAPI_ErrCode register_LinMasterTxEvent(uint32_t channelMappingID, uint8_t header, LINSendFrameHandler callback);
Description
- Register a callback function when a LIN frame is transmitted
parameters
-
channelMappingID LIN channel ID, 0 means the default channel ID of the current node
-
header LIN header to filter
-
callback Transmission complete handler (typedef void (LINSendFrameHandler)(EM_LINSendFrame_t))
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
void onLinMasterTx(EM_LINSendFrame_t* frame)
{
// Do something
}
uint32_t channelMappingID = 0;
uint8_t header = 0x3C;
register_LinMasterTxEvent(channelMappingID, header, onLinMasterTx);
9.5 Register LIN Master Pre-Transmission Callback
KAPI_ErrCode register_LinMasterPreTxEvent(uint32_t channelMappingID, uint8_t header, LINSendFrameHandler callback);
Description
- Register a callback function when a LIN frame is about to be transmitted
parameters
- channelMappingID LIN channel ID, 0 means the default channel ID of the current node
- header LIN header to filter
- callback Pre-transmission handler (typedef void (LINSendFrameHandler)(EM_LINSendFrame_t))
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
void onLinMasterPreTx(EM_LINSendFrame_t* frame)
{
// Do something
}
uint32_t channelMappingID = 0;
uint8_t header = 0x3C;
register_LinMasterPreTxEvent(channelMappingID, header, onLinMasterPreTx);
10. Digital
10.1 Set Digital Output Level
KAPI_ErrCode Do_Set(uint32_t channelMappingID, boolean lvl);
Description
- Set digital output level
parameters
- channelMappingID Digital output channel ID
- lvl
- 0 Low level
- 1 High level
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
Do_Set(0, 1);
10.2 Get Digital Input Status
KAPI_ErrCode Di_Get(uint32_t channelMappingID, boolean* value);
Description
- Get digital input status
parameters
- channelMappingID Digital input channel ID
- value Pointer to store input status
- 0 Low level
- 1 High level
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
boolean value;
Di_Get(0, &value);
11. Analog
11.1 Get Analog Input Voltage
KAPI_ErrCode Ai_Get(uint32_t channelMappingID, double* value);
Description
- Get analog input voltage
parameters
- channelMappingID Analog input channel ID
- value Pointer to store voltage value
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
double value;
Ai_Get(0, &value);
12. Other
12.1 Create Thread
KAPI_ErrCode create_Thread(ThreadFunction fun, void* pData, uint32_t interval_ms);
Description
- Create a thread
parameters
- fun Thread handler function (typedef void(*ThreadFunction)(void *pData))
- pData Thread handler parameter
- interval_ms Execution interval in milliseconds
Return
- 0 Success
- Other Failed
Usage
void onThread(void* pData)
{
// Do something
}
create_Thread(onThread, NULL, 1000);
12.2 Register Keyboard Key Press Callback
void (*resgister_onKey)(char key, void (*onKey)(void));
Description
- Register a callback function when a key is pressed
parameters
- key Key character
- onKey Callback function (typedef void (*onKey)(void))
Return
- void
Usage
void onKey(void)
{
// Do something
}
resgister_onKey('a', onKey);
12.3 System Message Output (To Host Application)
void show_system_message(const char* str);
Description
- Output a message to the host application
parameters
- str Message content
Return
- void
Usage
show_system_message("Hello World");
12.4 Console Message Output (To Mini Program Console)
void show_console_message(const char* str);
Description
- Output a message to the mini program console
parameters
- str Message content
Return
- void
Usage
show_console_message("Hello World");
12.5 Microsecond Delay (Busy Wait)
void delay_us(uint32 delaytime_us);
Description
- Delay for a specified time (Busy wait)
parameters
- delaytime_us Delay time in microseconds
Return
- void
Usage
delay_us(1000);
Note: This function should be used with caution, as it blocks the current thread until the delay period ends. Recommended to use timer instead of delay_us.
12.6 Millisecond Delay (Low CPU Usage)
void delay_ms(uint32 delaytime_ms);
Description
- Delay for a specified time (Low CPU usage)
parameters
- delaytime_ms Delay time in milliseconds
Return
- void
Usage
delay_ms(1000);
Note: This function should be used with caution, as it blocks the current thread until the delay period ends. Recommended to use timer instead of delay_ms.
12.7 Get Absolute Project Path
const char* GetAbsProjectPath();
Description
- Get the absolute path of the current project
parameters
- void
Return
- const char* Absolute path of the current project
Usage
const char* path = GetAbsProjectPath();
const wchar_t* GetAbsProjectPathW();
Description
- Get the absolute path of the current project (Wide character)
parameters
- void
Return
- const wchar_t* Absolute path of the current project (Wide character)
Usage
const wchar_t* path = GetAbsProjectPathW();